
Lokal Kraft aims to drive climate change together with e.g. property owners, associations and Malmö residents, based on geographical parts of the city of Malmö. The goal is to develop partnerships and working methods to maximize the climate effect of local development work, which will build on previous experiences of local development work. The starting point is the densification of Rosengård, but other urban areas with their own physical and socio-economic characteristics are included and provide a variety of situationally adapted solutions, which can be transferred to other areas.

The purpose and goal of the design phase is to explore and identify innovation capacity, solutions and policy obstacles, and to develop the existing partnership with more actors for the implementation of a long-term sustainable and climate-neutral district that promotes sustainable lifestyles, within the district and in surrounding neighborhoods. This is done within already established processes and collaboration between the municipality, municipal companies and construction actors in the work on the new district Tomtebo strand, and is supplemented with additional development capacity.

We want to move from an energy system that relies heavily on fossil fuels and increasingly on bioenergy and waste; to one that is entirely built around waste heat from electrified processes, heat pumps and "smart Al powered efficiency". We can save 1.4 million tons of CO2, while driving innovation, economic growth and democratic engagement at the community level.

The objective is to develop a roadmap for mobility hubs that will help create long-term, resilient yet flexible mobility solutions. The aim is to facilitate the realization of a coherent network of hubs not only at municipal level but ultimately to create a sustainable shared mobility system, contributing to a shift from private car use to a sustainable transport system based on shared mobility, public transport and active mobility.
Increased digitization makes cities increasingly vulnerable to cyber attacks, where computers are compromised by malicious actors in order to cause damage and disruption. The higher the degree of digitization, the more devastating the potential attacks. In order to mitigate cyber threats, vulnerabilities first need to be identified.

Sharing Cities Sweden is a national program for the sharing economy in cities. The program aims to put Sweden on the map as a country that actively and critically works with the sharing economy in cities. Sharing economy test beds in Stockholm, Gothenburg, Malmö and Umeå will develop sharing services and digital solutions/platforms. The test beds are complemented by a national node for coordination, national learning and international exchange.

To achieve the sustainability goals of the UN's Agenda 2030 initiative, municipalities must make their cities sustainable. Promoting innovation and new ways of collaboration can build a culture of experimentation that enables large-scale systemic change. By developing an innovation management support, the Accelerate project aims to increase the innovation and collaboration capacity of municipalities.

City as a Platform is an innovation initiative that brings together 18 municipalities to explore, test, implement and collaborate on common IoT platforms to support societal benefits in cities. The initiative will also ensure national anchoring and propose a national management model of a minimum framework for data platforms, including relevant standards.

City as a Platform is an innovation initiative that brings together 18 municipalities to explore, test, implement and collaborate on common IoT platforms to support societal benefits in cities. The initiative will also ensure national anchoring and propose a national management model of a minimum framework for data platforms, including relevant standards.
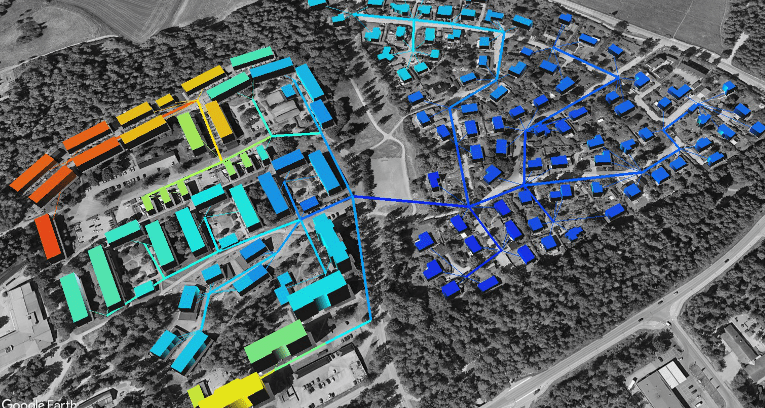
To reach set targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, while managing increased urbanization, cities need to find optimal strategies for transforming local energy use and supply. In this initiative, we develop an Urban Building Mobility and Energy Model (UBMEM) that will calculate and visualize energy and power demand and greenhouse gas emissions in the city as a basis for urban planning.
The initiative will develop digital solutions that make it possible to analyze energy consumption for both property management and healthcare operations. The aim is to identify and visualize opportunities for better energy use.
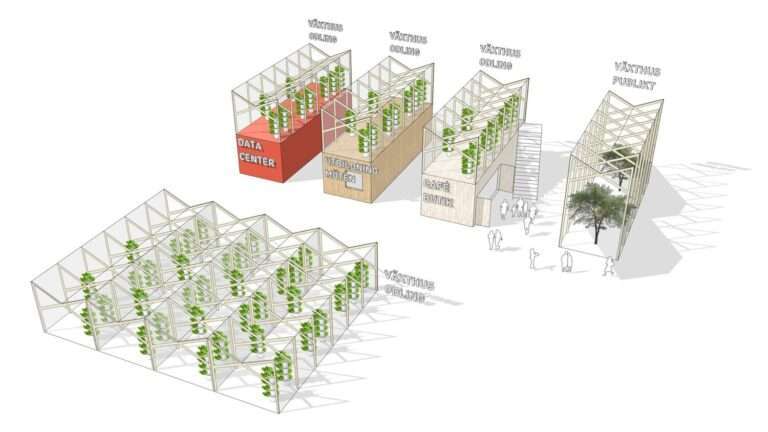
The initiative involves developing models for recycling waste heat from data centers for urban food production and soil cultivation in dense urban environments. The goal is to construct a first facility in Gothenburg with cultivation greenhouses closely integrated with the data center that is powered by waste heat and biological waste for climate-neutral food production in the city.

The initiative develops models for common digital infrastructure for resource flows that connect urban farming, real estate and district heating networks. This is the basis for small-scale urban food production that is climate-smart, efficient and profitable in industrial areas.

Under the initiative, the City of Stockholm and partners will carry out pilot installations of innovative fruit and vegetable growing systems in the city's industrial areas. These growing systems are expected to provide positive environmental effects and potential for civic engagement as well as new job opportunities for new arrivals.

The initiative will develop a dynamic visualization tool for more effective urban planning. The tool will provide better decision support by visualizing and communicating the consequences of urban development for the energy system. The tool is developed in consultation with Kiruna municipality, where the benefits will be significant due to the major change the city is facing.

The initiative will, based on Gävle, identify drivers and barriers for property owners (mainly small and medium-sized) to strengthen and preserve ecosystem services.

Car traffic in the city needs to be reduced - both to create a more attractive city and to reduce the climate impact of traffic. At the same time, mobility as a service is a growing trend. This initiative demonstrates "car-free living" in the Xplorion property at Södra Brunnshög in Lund by offering the EC2B mobility service to residents instead of car parking for private cars.

Achieving climate goals requires digital solutions, but with digitalization, the vulnerability of cities to cyberattacks is increasing. To prevent cyber attacks, vulnerabilities need to be identified. This is very difficult and requires an understanding of the city-wide system architecture and significant expertise in cybersecurity. This initiative will develop a threat modeling and attack simulation method for smart buildings, which play a key role in the future vision of livable cities.

The initiative will examine how urban planning can promote sustainable urban lifestyles. The focus is on knowledge about citizen participation and nudging as strategies to promote a more sustainable everyday life.

The initiative aims to capture innovative solutions from pilot projects in several municipalities. This is to accelerate climate-neutral urban development by enabling new solutions with great potential to become standard in new and existing areas more quickly.
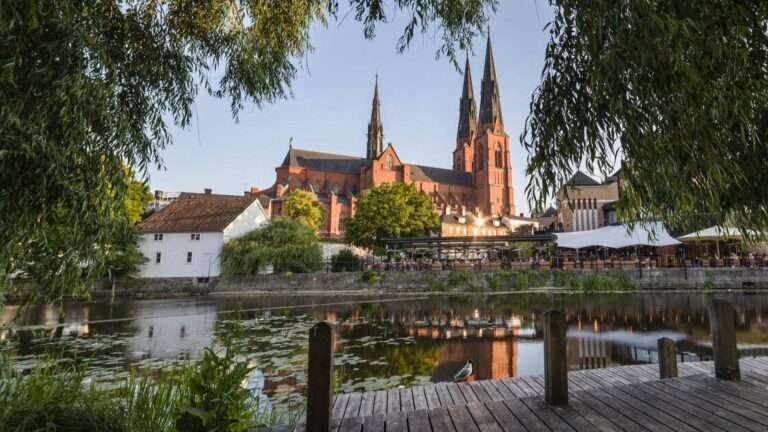

Klimatkampen Uppsala aims to accelerate the climate transition and facilitate more sustainable choices in everyday life for Uppsala residents. The initiative will engage and inform Uppsala residents in various ways about how they can reduce their climate impact.
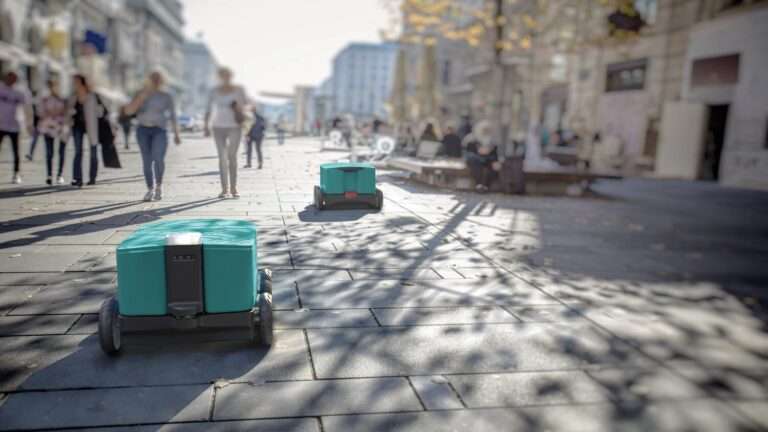

Based in Gothenburg, the initiative will explore how the environmental impact of urban logistics can be minimized with the widespread introduction of autonomous delivery robots.

The initiative is a demonstrator and includes initiatives for smart energy systems, circular resource flows and citizen engagement. By 2035, a socially sustainable and climate-positive district will be built with 4,500 homes and associated schools, preschools, healthcare, services and commerce. The initiative is based on the unique access that the non-profit foundation Stora Sköndal has as a demanding landowner.

The initiative will explore the possibility of establishing a large-scale test bed for citizens to produce and share energy services with each other. Citizens will also be able to deliver renewable electricity or power balancing to the energy market. There is a link to the test bed for the sharing economy that is being established within the framework of the Sharing Cities Sweden project.

MERiT is about anchoring sustainable travel among employers. The initiative examined different companies' measures regarding sustainability and business travel through a test of a digital tool at the City of Gothenburg and a follow-up of a travel agency procurement at RISE.

The initiative will develop climate-smart mobility solutions that are included in housing in the new Vårvik district in Trollhättan, where 1800 new homes will be built by 2030.

Mo-Bo is a housing concept with mobility services that solve residents' transportation needs in a socially, economically and ecologically sustainable way. Sharing economy and mobility services pave the way for innovative architecture where more people and goods can be transported by fewer vehicles, which means smarter use of resources and space.
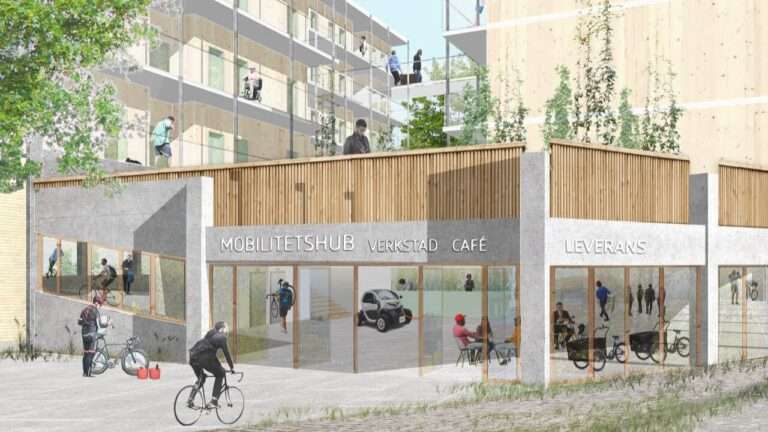

The initiative aims to change the way we live and travel in everyday life. With a holistic approach to mobility and housing, the initiative will increase resource efficiency through sharing services, digitization and innovative thinking about the form, operation and use of buildings. Smarter investments enable a new architecture that frees up space, saves resources and creates great value. This initiative is a continuation of a previous initiative focusing on new construction. In this new phase, the focus is on existing housing stock for greater scalability. The Rissne area in Sundbyberg is a test bed and the project handles the entire chain from municipal policy to residents' experiences and everyday life to pave the way for a broader system change.
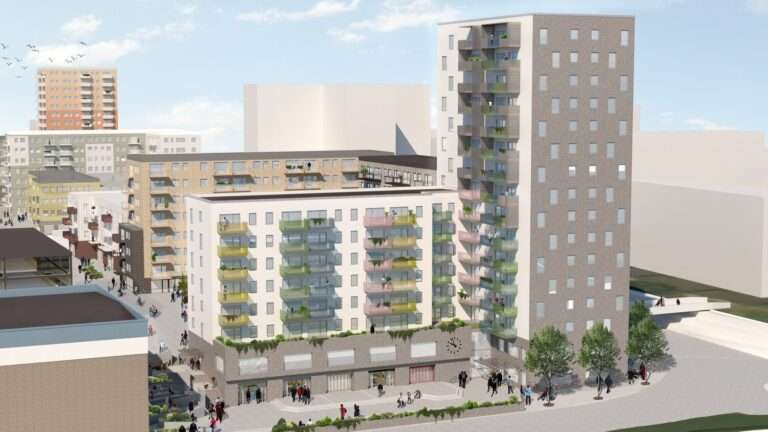

The initiative will explore how digitalization can affect the demand and supply of heated space in buildings, by introducing space-sharing services. It also examines new ways to measure energy use based on activity instead of per square meter. The focus is on Rosengård in Malmö as the basis for a full-scale test bed.

The initiative will develop methods and models for how public events can accelerate the climate transition in cities. The project brings together Sweden's largest live music festivals, Swedish sports and destinations for joint action with researchers. Since time immemorial, events have brought people together and sparked popular engagement. Producing and staging events requires energy, materials, water, food, waste management, areas that, like the travel and transportation of audiences and performers, have a significant climate impact. The number of events is increasing, while interest in events as a force for change for greater sustainability is growing. Important dimensions are changing behaviors and attitudes towards consumption and citizen engagement.

Building materials are a major source of climate emissions in our cities. The initiative focuses on new ways to reduce the extraction of new materials and to use materials already present in the urban environment, including through reuse from demolition and redevelopment projects.
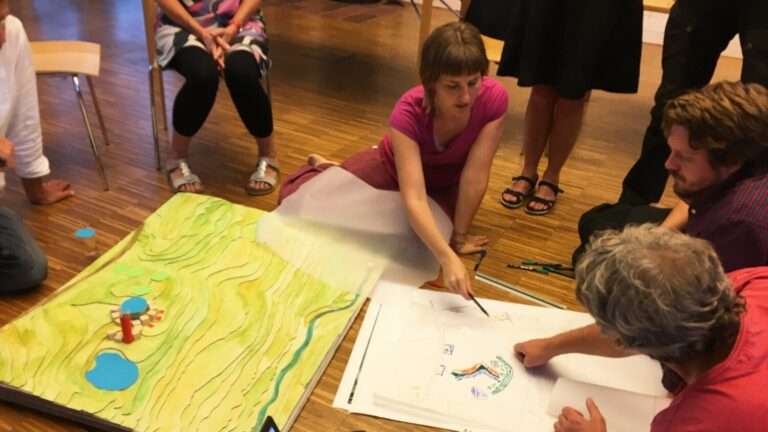

The initiative will help the town of Röstånga to become a fully renewable "plus energy town" in terms of energy. Knowledge and decision-making data on energy system solutions are produced for the residential environment R:ekobyn with 30 households with a view to replicability adapted to local conditions.
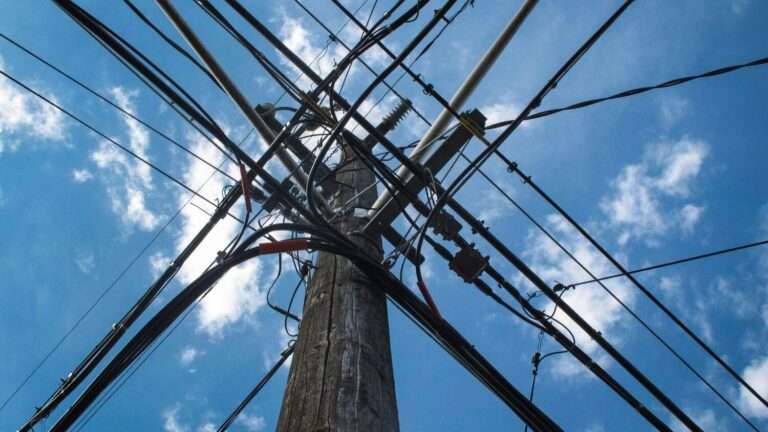

The initiative focuses on exploring the needs and limitations for smaller municipalities to use smart solutions for collaborative infrastructure. In Herrljunga and Kungälv, the initiative will explore opportunities to use city networks as a framework for digitizing the municipalities' water and electricity networks, but also other municipal/regional activities such as lighting, parking and public transport.

Air quality sensors are used to control indoor air and to inform the public about outdoor air. The initiative aims to improve the quality of measurement data for airborne particle sensors for better service to vulnerable road users and more efficient ventilation in buildings.

The initiative is part of the Sharing Cities Sweden program. Many sharing economy initiatives launched around the world have not succeeded as expected. Lack of knowledge about the underlying causes of (non) adoption, scaling and mainstreaming among users are the main reasons. The initiative aims to develop behavioral economic experiments that test, review and generate policy recommendations to promote sharing economy initiatives in cities.

The initiative is part of the Sharing Cities Sweden program. The understanding of the new business models is key to implementing "business model ecologies" in our cities. Therefore, analysis of business model ecologies is being carried out in several European cities. This effort makes it possible to estimate with high fidelity the performance of these new schemes, such as the car modeling business model.

The initiative, part of the Sharing Cities Sweden program, aims to explore the social drivers and potential of the sharing economy in communities and cities in Sweden. It will focus on how housing companies can facilitate sharing between tenants and provide space for sharing.

The initiative is part of the Sharing Cities Sweden program. The purpose of this initiative is to investigate whether digital sharing platforms based on a more user-centered sharing philosophy can solve the problems of the previous platforms, which tended to be more resource-centered.

The initiative, which is part of the Sharing Cities Sweden program, aims to reduce energy use and climate impact by developing the sharing economy in smaller cities. By using Karlstad and other smaller cities in dialog with Karlstad, the initiative will answer the question - what role can smaller cities and towns play in the sharing economy and how can their work be driven?

The initiative will explore ways to encourage more people to consume food in more environmentally and climate-smart ways. The goal is to understand how environmental information about different foods, together with smart approaches (nudging), can change consumer buying behavior.
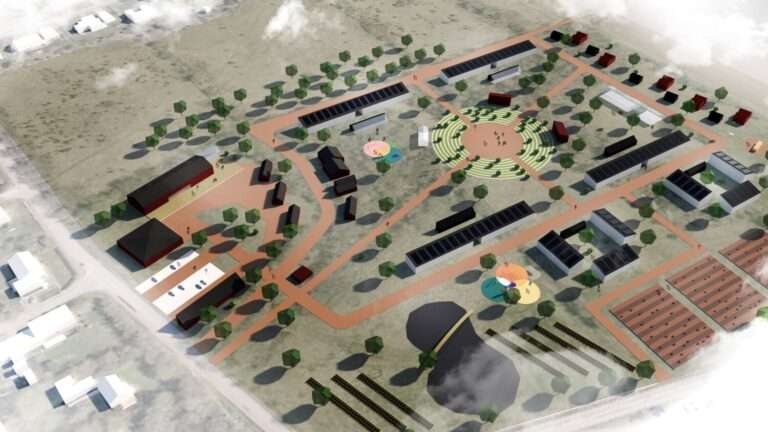

The Smart Village concept aims to build the neighborhood of the future with a high degree of energy self-sufficiency. The initiative aims to test the limits of how a modern area can be designed and provide opportunities for a lifestyle with near-zero emissions while creating new conditions for social interaction.

The initiative will examine the conditions for a demonstration project for flexible energy systems in buildings based on solar electricity, local storage and controllable loads in the newly established district of Brunnshög in Lund municipality.

The initiative will explore how social and climate impacts can be measured and calculated in sustainable bond solutions, thereby helping to mobilize capital. The market for sustainable investments is growing. The aim is to open up investments in new models and solutions that can accelerate the transition to low-carbon cities. Today, few bond solutions support a holistic approach to smart, sustainable cities. The initiative will create a framework for a sustainable city bond.

This initiative has two objectives. It will provide a policy-relevant overview of experiences gained as a basis for systematic learning on how system innovation in sustainable urban development has been developed in practice. It will also help to further develop these experiences and lessons learned with a focus on a new model of governance for climate transition in cities and municipalities. Governance refers to when an authority, such as a municipality, needs to go beyond what it has control over to bring about change, in this case in the form of collaboration with business, civil society and academia on climate change.
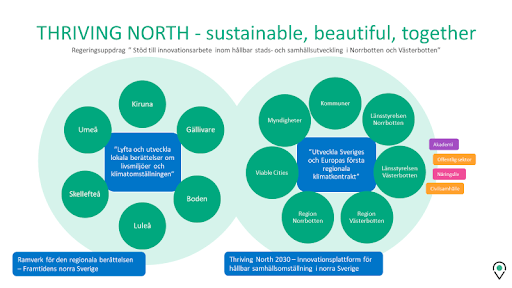
In 2022, Viable Cities has been responsible for a government assignment "Support for innovation work in sustainable urban and community development in Norrbotten and Västerbotten" with the working name Thriving North. The assignment identified six municipalities (Kiruna, Gällivare, Boden, Luleå, Skellefteå and Umeå) and actors in Västerbotten and Norrbotten (county administrative boards and regions). The government assignment was divided into four partial deliveries.

This feasibility study aims to explore how the smart city can best support its citizens and connected things in terms of digital infrastructure. How are we connected to services and functions in 2030? What services and business models might exist? What are the needs and requirements for accessibility and security? How does the network become more robust against external and internal impacts?

The initiative will examine the conditions for developing the Urban ICT Arena test bed in Kista into a quadruple helix environment, with collaboration between academia, business, public organisations and civil society. With a focus on the link to local civil society, the initiative will address the energy challenge to accelerate the transition to a sustainable city.

The initiative will create conditions for various companies, associations, research and public activities to benefit from open data from the ectogrid™ energy system. By making ectogrid™ data available, digitalization and citizen involvement can contribute to increased energy system optimization, e.g. by balancing energy types and loads.
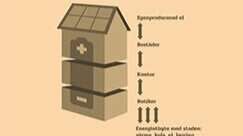
The initiative will shorten the links between research and practice in working with three-dimensional (3D) building layout to accommodate multiple owners and many functions in the same building. This creates both opportunities and challenges for energy optimization (e). The initiative focuses on bringing together researchers with specifiers and implementers in three urban development projects.




































